H.264 – An Introduction
H.264 (also called AVC, or Advanced Video Coding) is an industry standard for video compression that allows for the recording, compression, and distribution of digital video content.
It works by processing frames of video using a block-oriented, motion-compensation-based video compression standard. Those units are called macroblocks. Macroblocks (see image below) typically consist of 16x16 pixel samples that can be subdivided into transform blocks, and may be further subdivided into what are known as prediction blocks.
While that might sound confusing, here’s what you need to know: The H.264 algorithm can substantially lower bitrates better than previous standards, and is widely used by streaming internet sources like Vimeo, YouTube, iTunes, and more.
How Is H.265 Different?
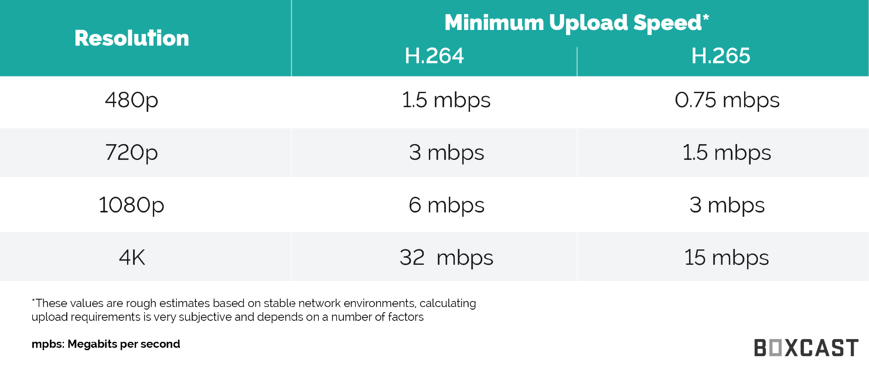
H.265 is more advanced than H.264 in several ways. The main difference is that HEVC allows for further reduced file size, and therefore reduced required bandwidth, of your live video streams.
Unlike H.264 macroblocks, H.265 processes information in what’s called coding tree units (CTUs). Whereas macroblocks can span 4x4 to 16x16 block sizes, CTUs can process as many as 64x64 blocks, giving it the ability to compress information more efficiently.
In addition to the larger CTU sizes, HEVC also has better motion compensation and spatial prediction than AVC does. This means that HEVC requires more advanced hardware, such as the BoxCaster Pro, to be able to compress the data. Fortunately, however, it also means that viewers with H.265 compatible devices will require less bandwidth and processing power to decompress that data and watch a high-quality stream. This also enables the streaming of 4K video over common network speeds.